Arrays
一维数组:
1
| int arr[5] = {4, 12, 7, 15, 9};
|
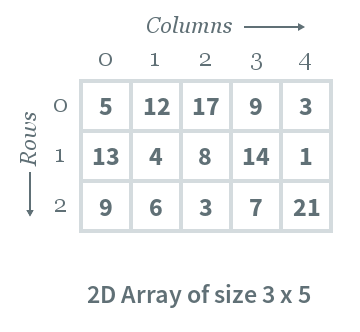
二维数组:N*M, 表示N行M列。
1
| int arr[3][5] = {{5, 12, 17, 9, 3}, {13, 4, 8, 14, 1}, {9, 6, 3, 7, 21}};
|
Stacks
栈是只允许后进先出(LIFO)的动态数据结构。没有固定的大小。
栈只允许一端操作,出栈叫pop(),入栈叫push()。
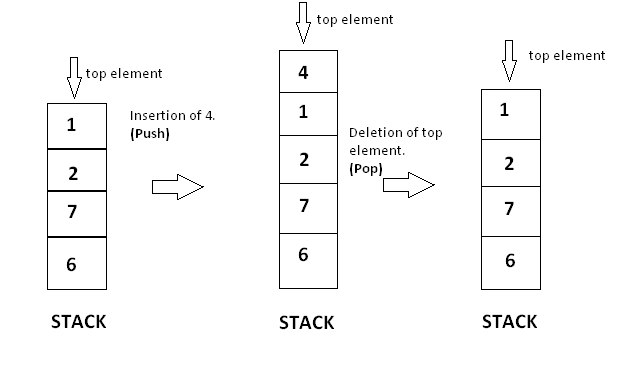
push()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
| void push (int stack[ ] , int x , int n) { if ( top == n-1 ) { cout << “Stack is full.Overflow condition!” ; } else{ top = top +1 ; stack[ top ] = x ; } }
|
pop()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
| void pop (int stack[ ] ,int n ) { if( isEmpty ( ) ) { cout << “Stack is empty. Underflow condition! ” << endl ; } else { top = top - 1 ; } }
|
Queues
队列是满足先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构。数据总是从尾端进入,从头部出去。
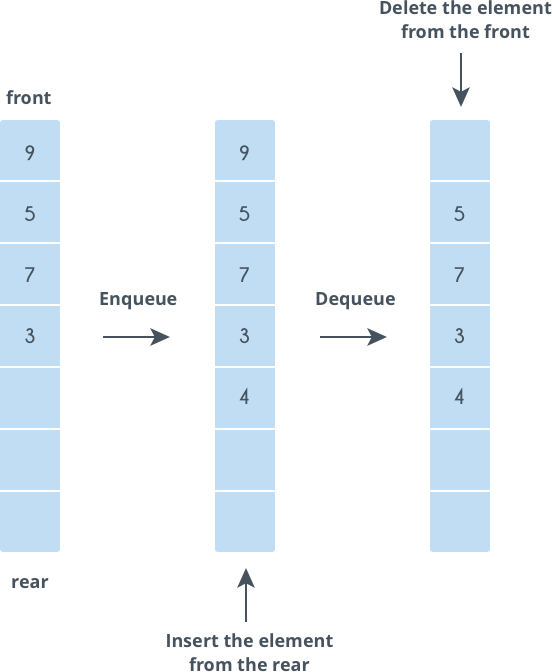
enqueue()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| void enqueue(int queue[], int element, int& rear, int arraySize) { if(rear == arraySize) printf(“OverFlow\n”); else{ queue[rear] = element; rear++; } }
|
dequeue()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| void dequeue(int queue[], int& front, int rear) { if(front == rear) printf(“UnderFlow\n”); else { queue[front] = 0; front++; } }
|
size()
1 2 3
| int size(int front, int rear) { return (rear - front); }
|
isEmpty()
1 2 3
| bool isEmpty(int front, int rear) { return (front == rear); }
|
双端队列,两端都可以进行出和进操作。
循环队列,解决空间浪费问题。
循环队列
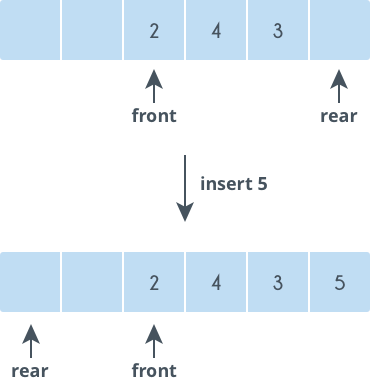
enqueue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
| void enqueue(int queue[], int element, int& rear, int arraySize, int count) { if(count == arraySize) printf(“OverFlow\n”); else{ queue[rear] = element; rear = (rear + 1)%arraySize; count = count + 1; } }
|
dequeue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| void dequeue(int queue[], int& front, int count) { if(count == 0) printf(“UnderFlow\n”); else { queue[front] = 0; front = (front + 1)%arraySize; count = count - 1; } }
|
Hash Tables
哈希(散列)是一种能够在相似的元素集合中找到唯一标示的元素的技术。
使用哈希函数,将大的关键字转换成小的关键字,然后将值通过关键字存储在特定的数据结构中,叫做哈希表。
理想情况下:O(1)
哈希2步走:
- 元素通过哈希函数,转换成哈希表的索引。
- 将元素存储在索引对应的哈希表中。
1 2
| hash = hashfunc(key) index = hash % array_size
|
好的哈希函数:
- 容易计算。
- 分布均匀,避免堆积。
- 更少的哈希冲突。
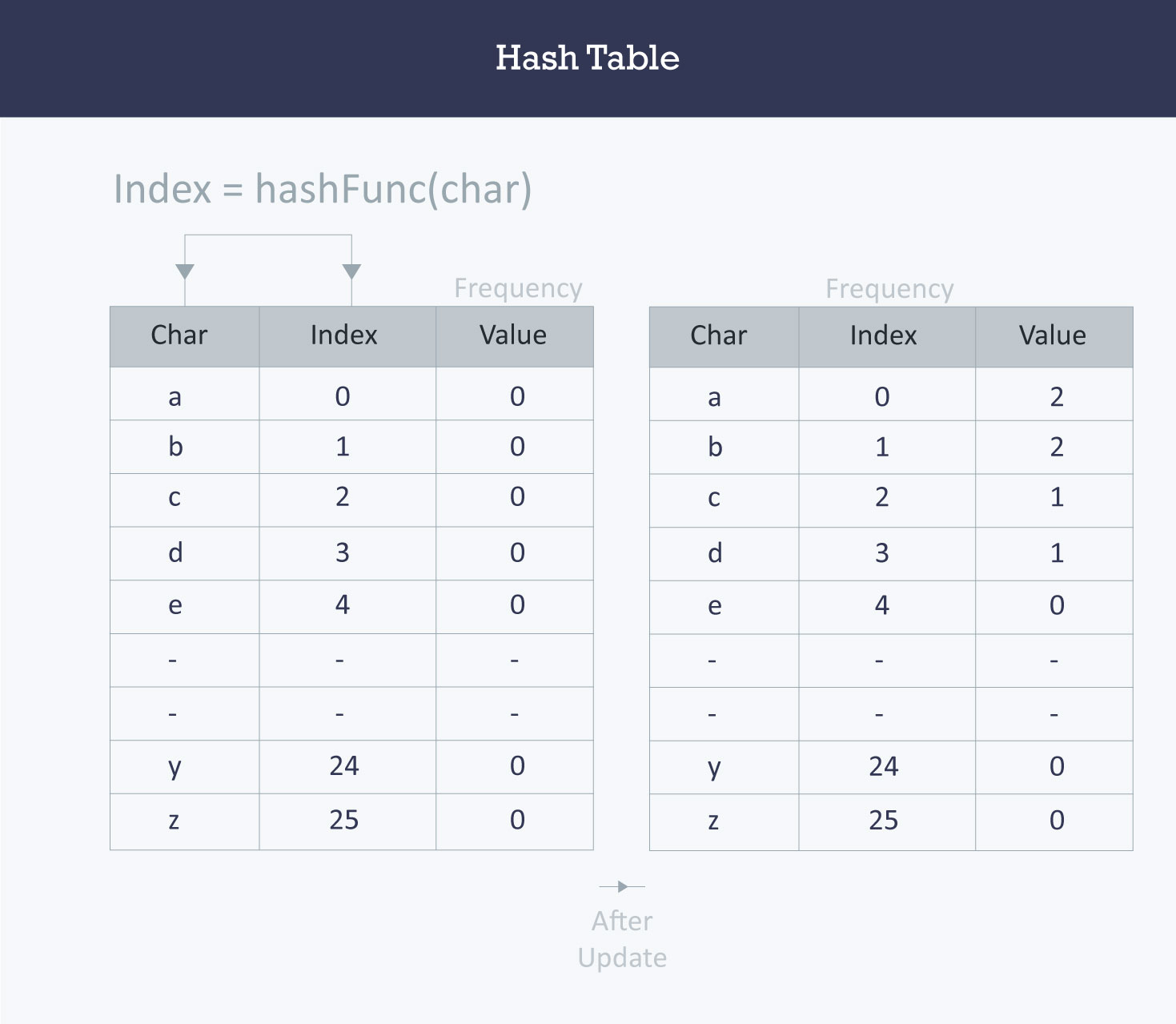
example:统计字符串中各个字符的频率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
| int Frequency[26]; int hashFunc(char c) { return (c - ‘a’); } void countFre(string S) { for(int i = 0;i < S.length();++i) { int index = hashFunc(S[i]); Frequency[index]++; } for(int i = 0;i < 26;++i) cout << (char)(i+’a’) << ‘ ‘ << Frequency[i] << endl; }
|
解决哈希冲突
分离链表发
哈希表的每一个元素,都是一张链表。当发生哈希冲突时,将它们同时放在链表里。
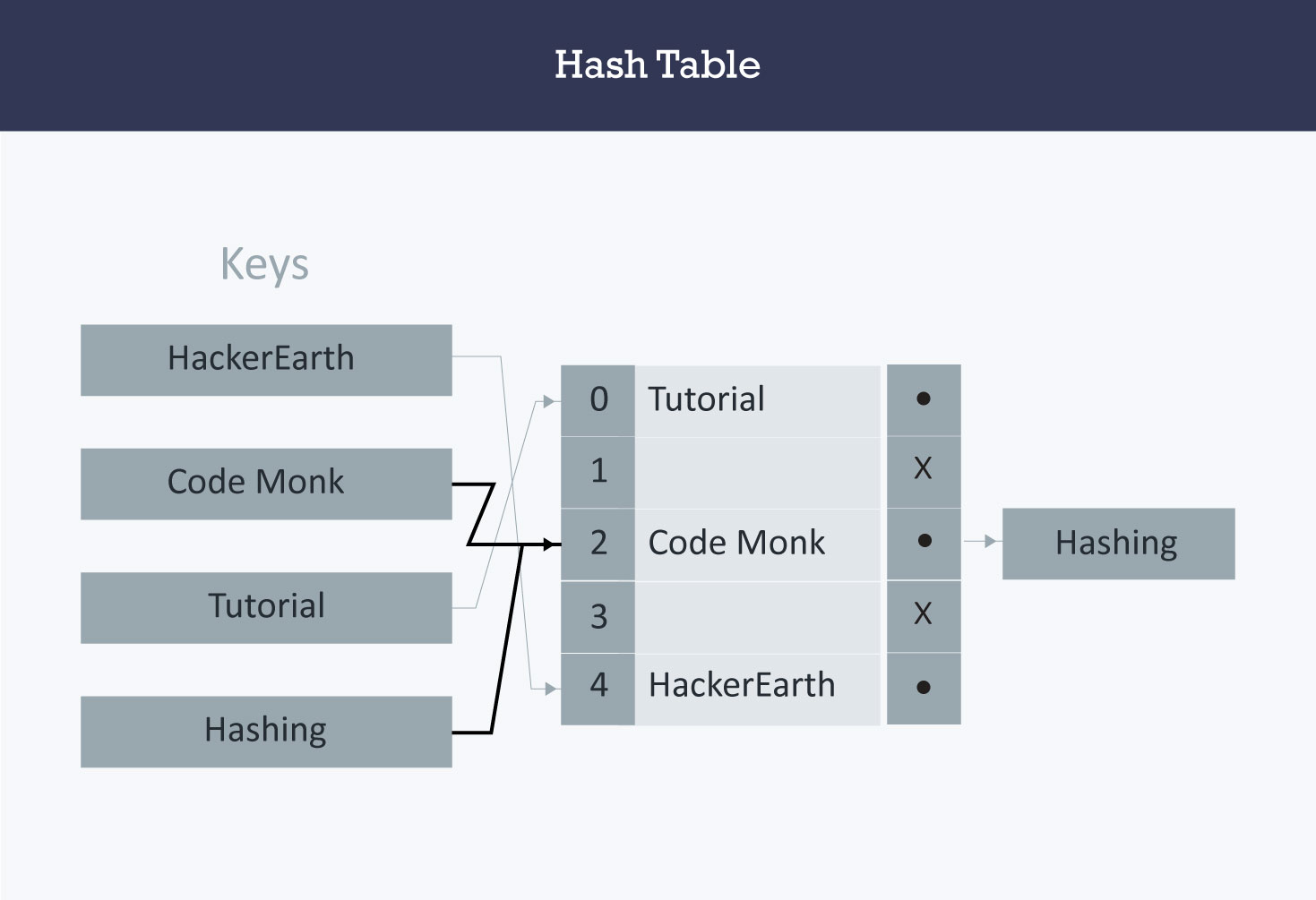
定义一个哈希链表
1 2
| vector <string> hashTable[20]; int hashTableSize=20;
|
insert
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| void insert(string s) { int index = hashFunc(s); hashTable[index].push_back(s); }
|
search
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
| void search(string s) { //Compute the index by using the hash function int index = hashFunc(s); //Search the linked list at that specific index for(int i = 0;i < hashTable[index].size();i++) { if(hashTable[index][i] == s) { cout << s << " is found!" << endl; return; } } cout << s << " is not found!" << endl; }
|
邻接地址法(开地址法)
如果当前地址没有元素,就存放。如果已经有了,就去向后找。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| //线性探测 index = index % hashTableSize index = (index + 1) % hashTableSize index = (index + 2) % hashTableSize index = (index + 3) % hashTableSize and so on…
|
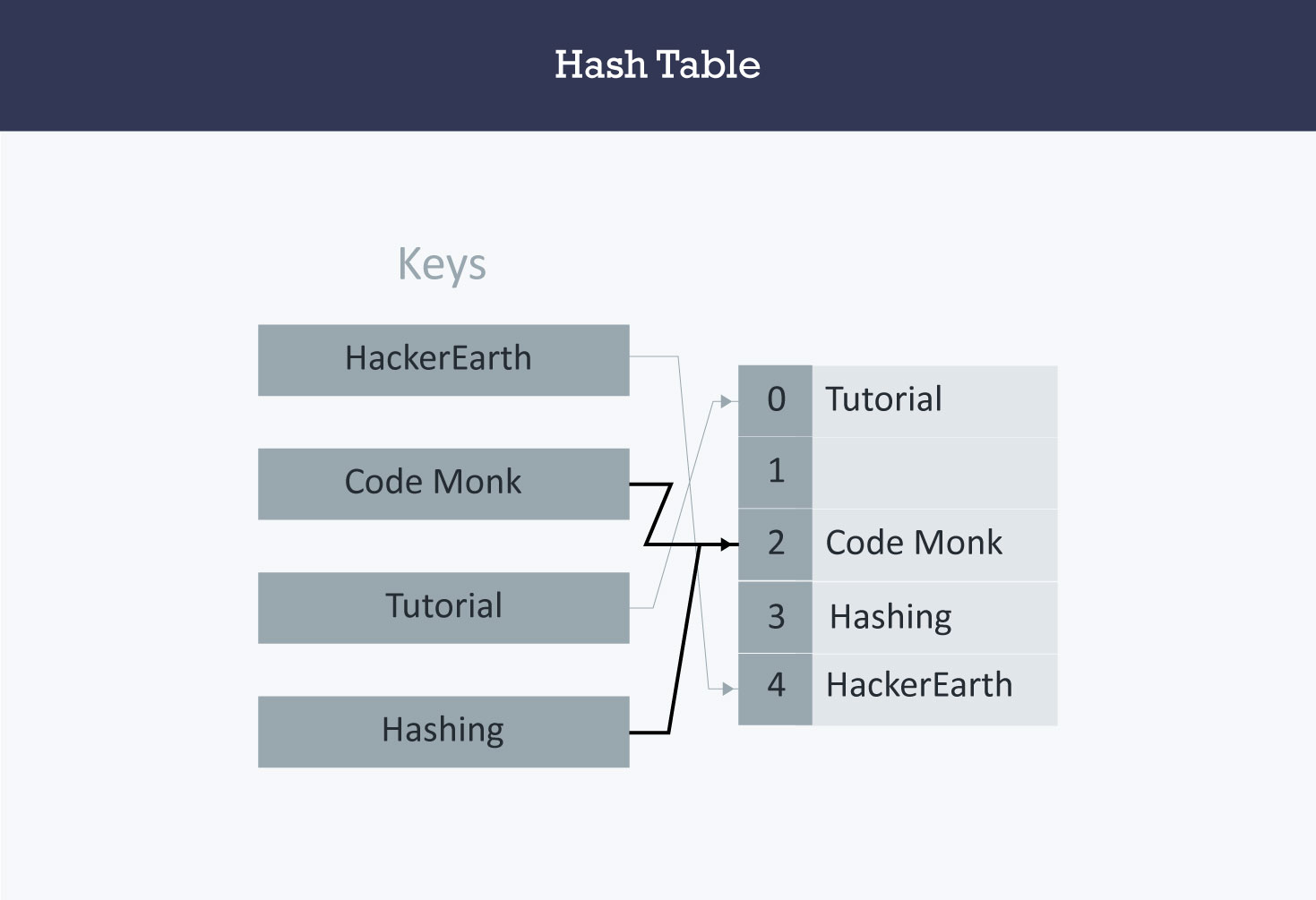
定义哈希表
1 2
| string hashTable[21]; int hashTableSize = 21;
|
insert
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| void insert(string s) { int index = hashFunc(s); while(hashTable[index] != "") index = (index + 1) % hashTableSize; hashTable[index] = s; }
|
search
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
| void search(string s) { int index = hashFunc(s); while(hashTable[index] != s and hashTable[index] != "") index = (index + 1) % hashTableSize; if(hashTable[index] == s) cout << s << " is found!" << endl; else cout << s << " is not found!" << endl; }
|
1 2 3 4 5
| //二次探测 index = index % hashTableSize index = (index + 12) % hashTableSize index = (index + 22) % hashTableSize index = (index + 32) % hashTableSize
|
哈希表应用:
Linked List
单链表定义:
1 2 3 4
| struct LinkedList{ int data; struct LinkedList *next; };
|


创建node
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| typedef struct LinkedList *node; node createNode(){ node temp; temp = (node)malloc(sizeof(struct LinkedList)); temp->next = NULL; return temp; }
|
addNode
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
| node addNode(node head, int value){ node temp,p; temp = createNode(); temp->data = value; if(head == NULL){ head = temp; } else{ p = head; while(p->next != NULL){ p = p->next; } p->next = temp; } return head; }
|
Trees
Binary/N-ary Trees
二叉树由多个节点组成,每一个节点满足:
- 节点保存数据
- 左指针指向左节点
- 右指针指向右节点
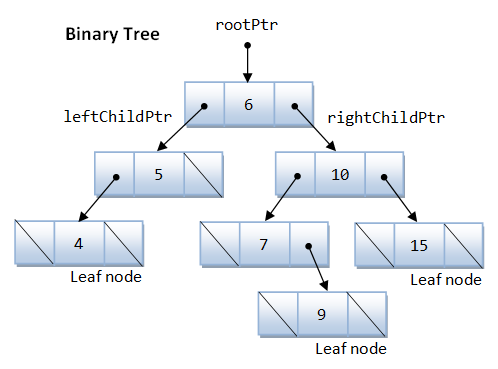
Root: Top node in a treeChild: Nodes that are next to each other and connected downwardsParent: Converse notion of childSiblings: Nodes with the same parentDescendant: Node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to childAncestor: Node reachable by repeated proceeding from child to parent.Leaf: Node with no childrenInternal node: Node with at least one childExternal node: Node with no children
定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6
| struct node { int data; struct node * left; struct node * right; };
|
创建节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| struct node * newnode(int element) { struct node * temp=(node * )malloc(sizeof(node)); temp->data=element; temp->left=temp->right=NULL; return temp; }
|
计算树的高度:O(n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
| int maxDepth(struct node* node) { if (node==NULL) return 0; else { int lDepth = maxDepth(node->left); int rDepth = maxDepth(node->right); if (lDepth > rDepth) return(lDepth+1); else return(rDepth+1); } }
|
树的应用:
Binary Search Tree
二叉搜索树是满足以下条件的二叉树。
- 所有节点的左子树的节点都<=当前节点。
- 所有节点的右子树的节点都>=当前节点。
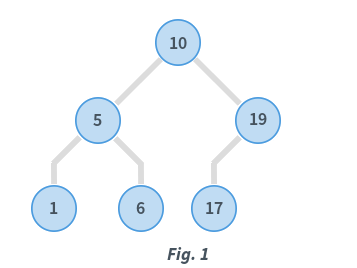
遍历树的三种方式:(以root节点的顺序命名)
先序遍历: root->left->right
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| void preorder(struct node*root) { if(root) { printf("%d ",root->data); preorder(root->left); preorder(root->right); } }
|
后序遍历: left->right->root
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| void postorder(struct node*root) { if(root) { postorder(root->left); postorder(root->right); printf("%d ",root->data); } }
|
中序遍历:left->root->right
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
| void inorder(struct node*root) { if(root) { inorder(root->left); printf("%d ",root->data); inorder(root->right); } }
|
树的中序遍历产生有序的遍历结合
插入BST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
| struct node* insert(struct node* root, int data) { if (root == NULL) return newNode(data); else { if (data <= root->data) root->left = insert(root->left, data); else root->right = insert(root->right, data); return root; } }
|
Heaps/Priority Queues
大堆:任何父节点的值都大于其子孙节点。
假设ROOT映射到数组下标1。
子节点可以通过(h - 1) * 2 和 (h - 1) * 2 + 1 映射到数组下标。h是父节点下标。
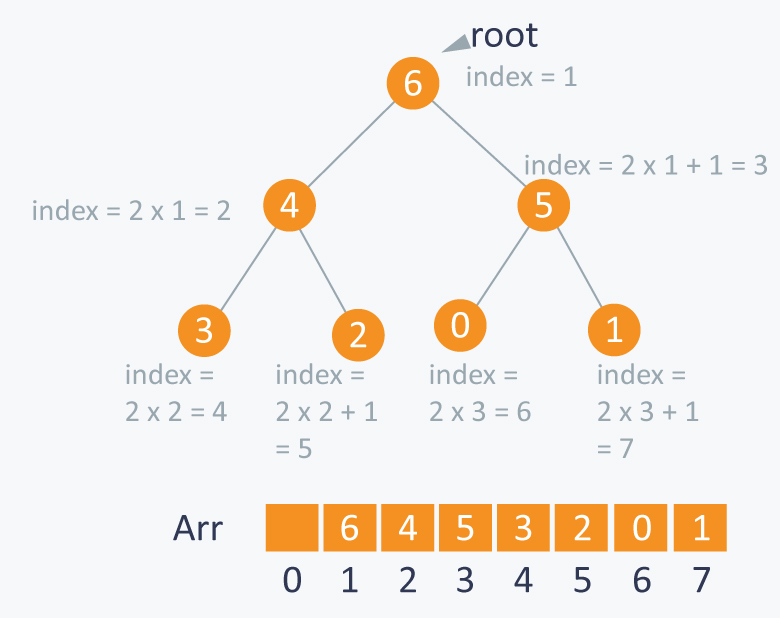
将下标是i的节点大堆化,N是数组大小。O(logN)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
| void max_heapify (int Arr[ ], int i, int N) { int left = 2*i int right = 2*i +1 if(left<= N and Arr[left] > Arr[i] ) largest = left; else largest = i; if(right <= N and Arr[right] > Arr[largest] ) largest = right; if(largest != i ) { swap (Arr[i] , Arr[largest]); max_heapify (Arr, largest,N); } }
|
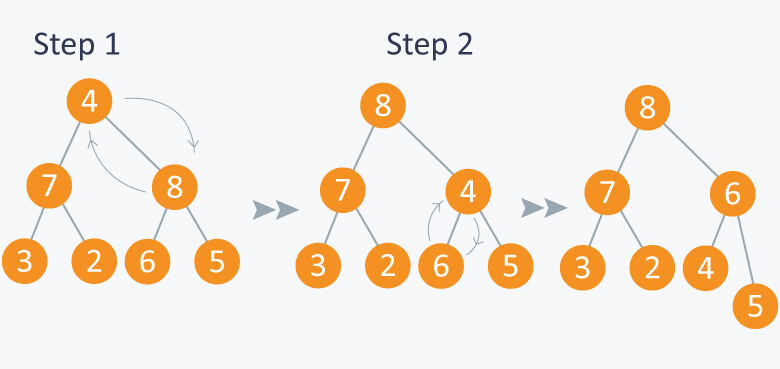
从数组构建大堆:因为arr[n/2+1]~arr[n]是叶子节点。O(N)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| void build_maxheap (int Arr[ ]) { for(int i = N/2 ; i >= 1 ; i-- ) { max_heapify (Arr, i) ; } }
|
堆排序 O(Nlog(N))`
排序过程:
- 构建大堆树
- 将root(当前最大节点)与数组最后一个节点交换。这时,最后一个节点已经有序。
- 数组大小减1,重复执行1,2步骤。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| void heap_sort(int Arr[ ]) { int heap_size = N; build_maxheap(Arr); for(int i = N; i>=2 ; i-- ) { swap(Arr[ 1 ], Arr[ i ]); heap_size = heap_size-1; max_heapify(Arr, 1, heap_size); } }
|
图解:
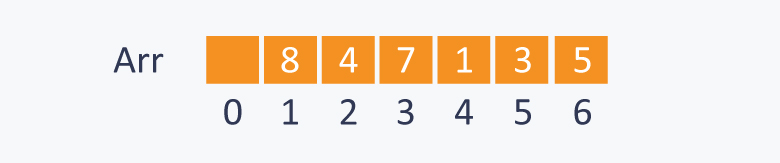
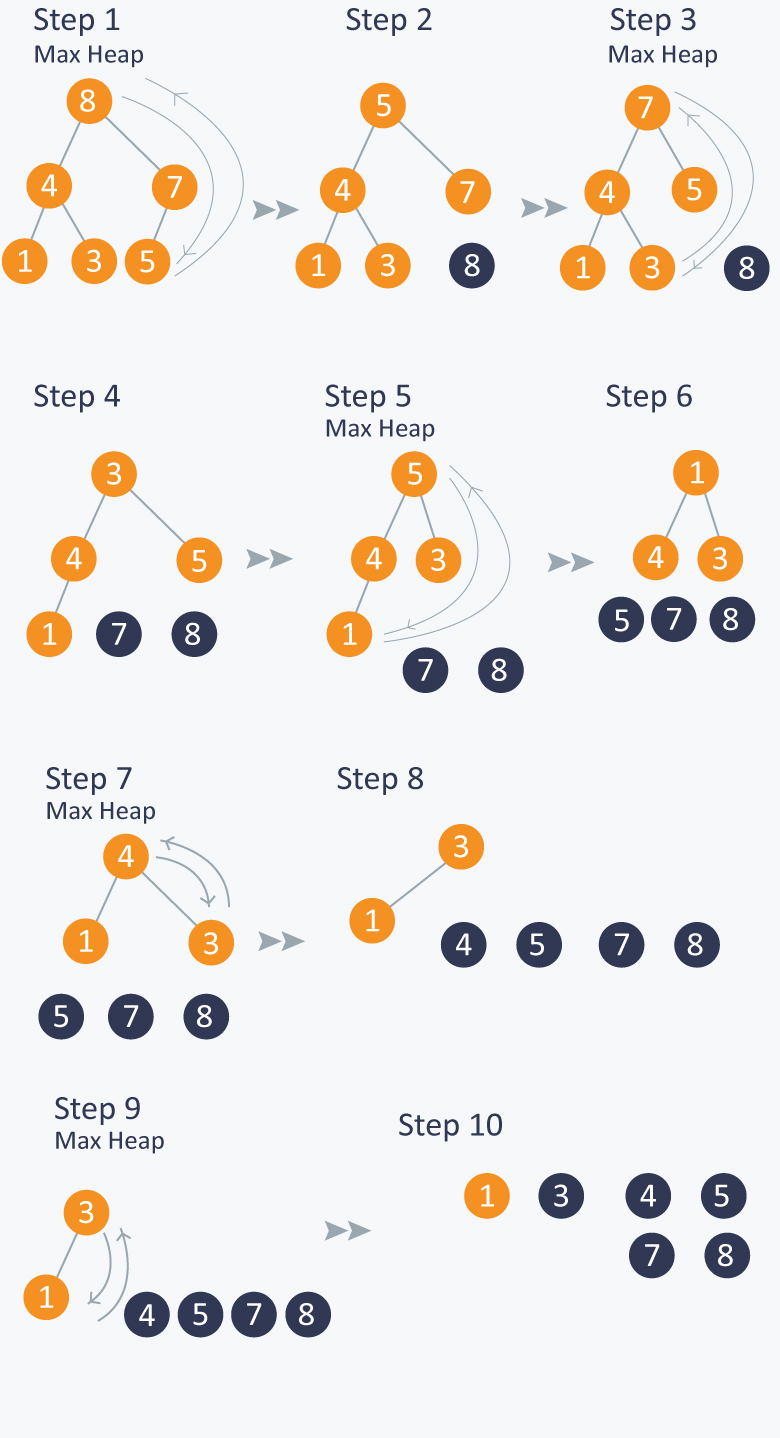
优先级队列
优先级队列每次都要求优先级最高的先出站。我们可以创建一个对应的堆。
将对最大值放到根节点,然后出队列。最后一个元素放到根节idan,然后通过上面的max_heapify(Arr, 1, heap_size),调整堆。
出队列的操作:O(logN)
Trie(Keyword Tree)
字符串处理是重要和常见的话题。
如:
Tries是基于字符串前缀的数据结构。
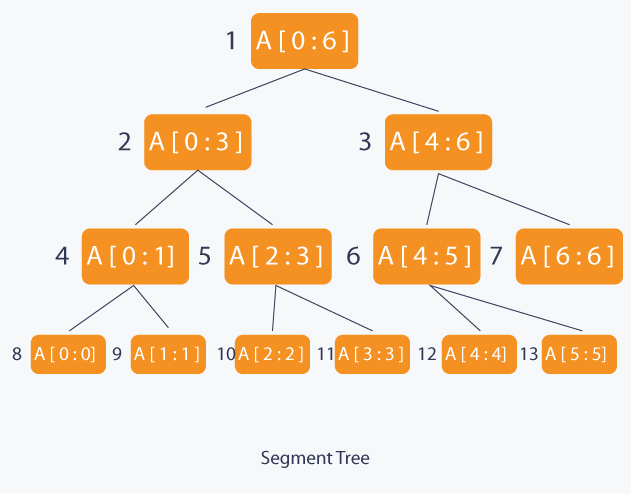
Segment Trees
分段树用于范围查找,如计算数组L到R之间所有元素的和。
比如:
一个N个元素的数组:
- 根节点
A[0:N-1]
- 叶子节点
A[i],0<=i<N
- 中间节点
A[i,j], 0<=i<j<N
- 树的高度
log2N,树节点总数2*N-1
Disjoin Data
并查集
如:有一个数组
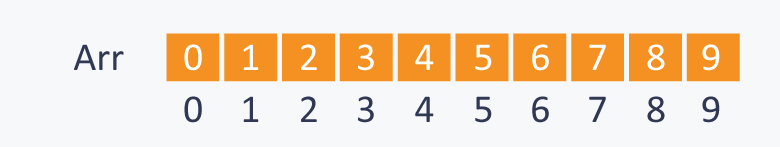
执行两种操作:
- Find(A, B) : 检查arr[A]==arr[B]?
- Union(A, B): 将arr[B]的值赋给arr[A]
执行以下操作:
Union(2,1)
Union(4,3)
Union(8,4)
Union(9,3)
Union(6,5)
将分成5个集合
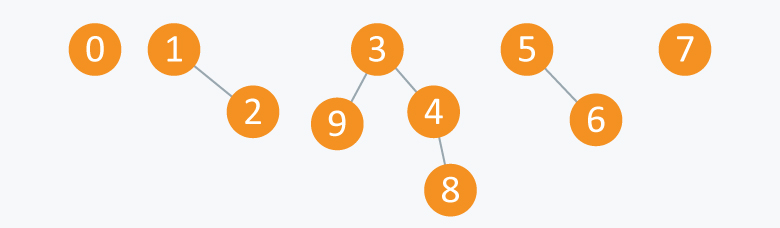
数组变成
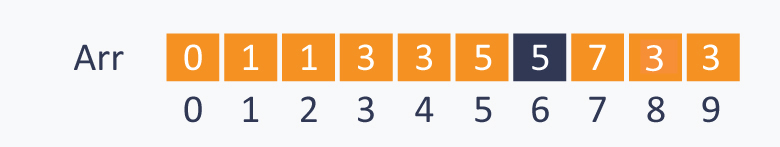
初始化:有N个集合,每个集合一个元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
| void initialize( int Arr[ ], int N) { for(int i = 0;i<N;i++) Arr[ i ] = i ; } bool find( int Arr[ ], int A, int B) { if(Arr[ A ] == Arr[ B ]) return true; else return false; } void union(int Arr[ ], int N, int A, int B) { int TEMP = Arr[ A ]; for(int i = 0; i < N;i++) { if(Arr[ i ] == TEMP) Arr[ i ] = Arr[ B ]; } }
|