概述
图是表示对象之间两两关系的数据结构。
图可以直观的由节点和边表示。
无向图:所有的边都是双向的。
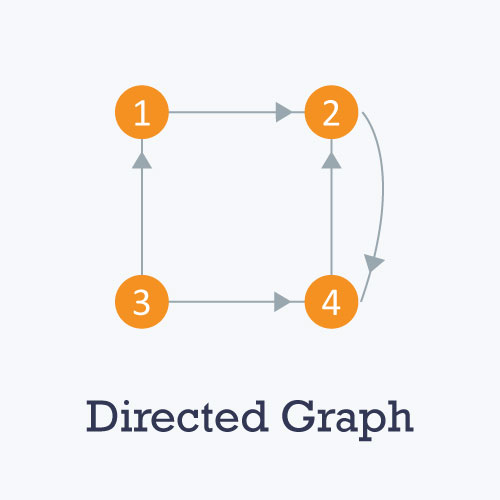
有向图:所有的边都是单向的。
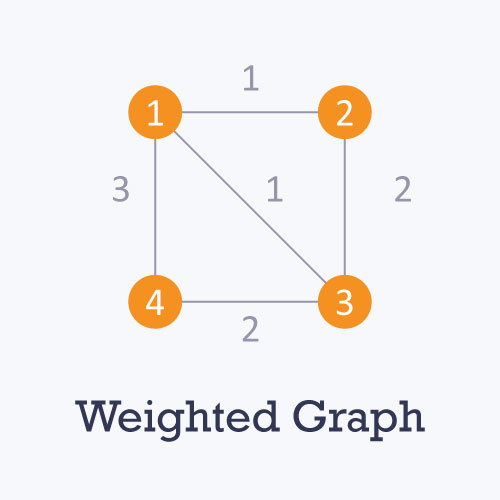
权重的图:图的每一条边是有权重的。
如1->4->3的权重:3+2=5
有环图:从一个节点出发,能够回到同一个节点,这个路径就是一个环,不包含环的叫无环图。
树是无向无环图
图的表示:
邻接矩阵
用一个N*N的二维数组表示N个节点之间的关系。
如:
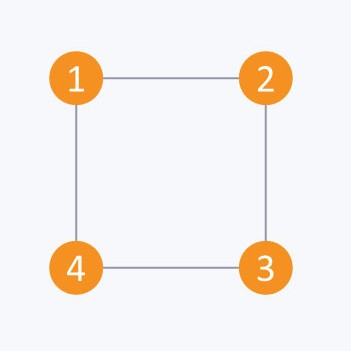
以下的图可以用矩阵表示:0表示节点i,j直接没有连接关系,1表示连接关系
>
i/j: 1 2 3 4
1 : 0 1 0 1
2 : 1 0 1 0
3 : 0 1 0 1
4 : 1 0 1 0
查找$ O(1) $, 空间$ O(V^2) $
邻接链表
如:
以下的图可以表示为
>
A1 → 2
A2 → 4
A3 → 1 → 4
A4 → 2
空间复杂度$ O(V+E) $
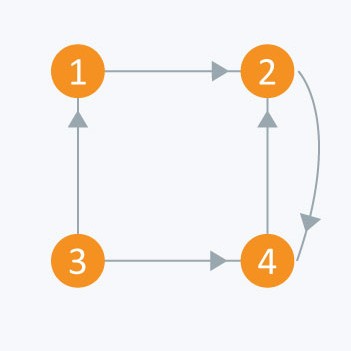
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search)
BFS广度优先搜索是遍历图的一种方法。时间复杂度$ O(V+E) $
- 首先遍历当前节点层的节点
- 然后向下搜索
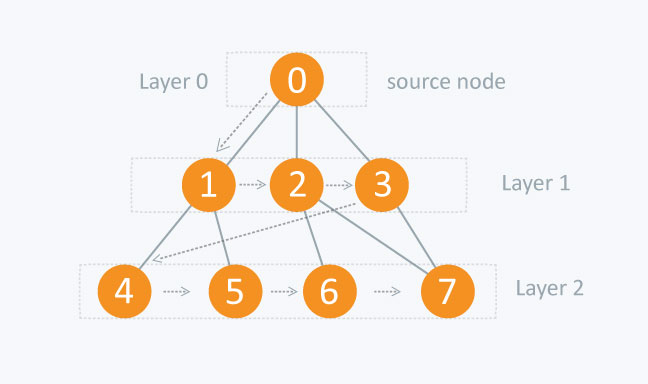
由于可能存在环,所有需要设置一个标志位。表示是否被访问过。
我们用一个队列(FIFO)来保存节点。
伪代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
| BFS (G, s) let Q be queue. Q.enqueue( s ) mark s as visited. while ( Q is not empty) v = Q.dequeue( ) for all neighbours w of v in Graph G if w is not visited Q.enqueue( w ) mark w as visited.
|
过程演示

应用:计算树种节点的高度
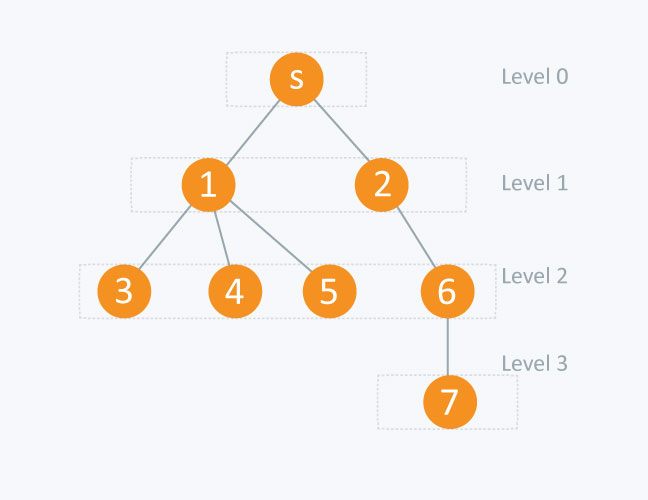
实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
| vector <int> v[10] ; int level[10]; bool vis[10]; void bfs(int s) { queue <int> q; q.push(s); level[ s ] = 0 ; vis[ s ] = true; while(!q.empty()) { int p = q.front(); q.pop(); for(int i = 0;i < v[ p ].size() ; i++) { if(vis[ v[ p ][ i ] ] == false) { level[ v[ p ][ i ] ] = level[ p ]+1; q.push(v[ p ][ i ]); vis[ v[ p ][ i ] ] = true; } } } }
|
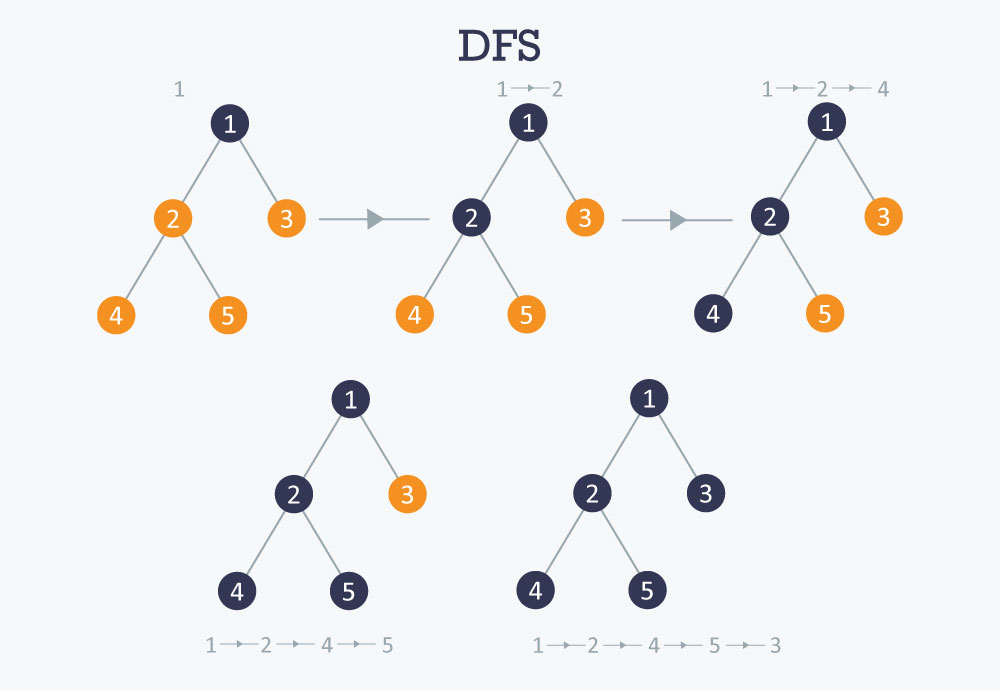
深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)
DFS深度优先搜索利用回溯法。时间复杂度$ O(V+E) $
- 一直向后查找子节点
- 不再有任何子节点,回溯。
我们使用栈来保存节点,首先选一个节点,将相邻的节点都入栈,然后从栈中去一个节点,重复之前的操作,直到栈为空。
伪代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
| DFS-iterative (G, s): let S be stack S.push( s ) mark s as visited. while ( S is not empty): v = S.top( ) S.pop( ) for all neighbours w of v in Graph G: if w is not visited : S.push( w ) mark w as visited DFS-recursive(G, s): mark s as visited for all neighbours w of s in Graph G: if w is not visited: DFS-recursive(G, w)
|
图解
应用:查找连通分量
连通分量:通过边连接的节点集合。
如:
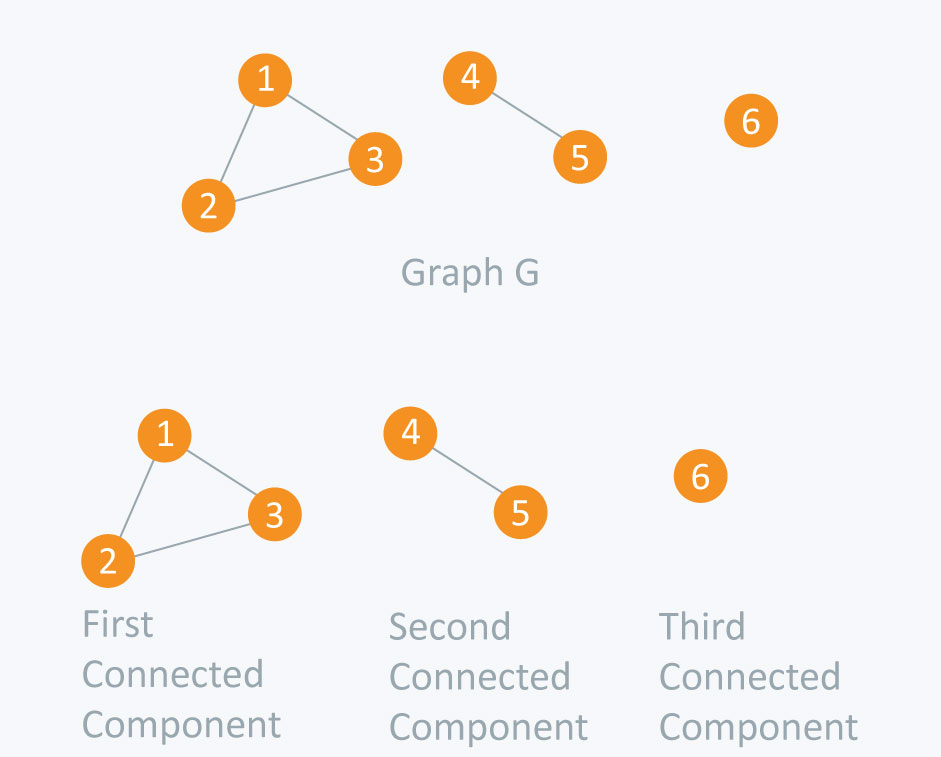
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
| #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; vector <int> adj[10]; bool visited[10]; void dfs(int s) { visited[s] = true; for(int i = 0;i < adj[s].size();++i) { if(visited[adj[s][i]] == false) dfs(adj[s][i]); } } void initialize() { for(int i = 0;i < 10;++i) visited[i] = false; } int main() { int nodes, edges, x, y, connectedComponents = 0; cin >> nodes; cin >> edges; for(int i = 0;i < edges;++i) { cin >> x >> y; adj[x].push_back(y); adj[y].push_back(x); } initialize(); for(int i = 1;i <= nodes;++i) { if(visited[i] == false) { dfs(i); connectedComponents++; } } cout << "Number of connected components: " << connectedComponents << endl; return 0; }
|
input
output
1
| Number of connected components: 3
|
最小生成树(Minimum Spanning Tree)
用G=(V,E)表示V个节点,E条边的图。生存树是G的子集。
生成树的代价是所有边权重的和。最小生成树是代价最小的生成树。
应用于网络设计、图像分割、手写识别、群集分析、邮递员问题、多端最小割问题和加权最少费和。
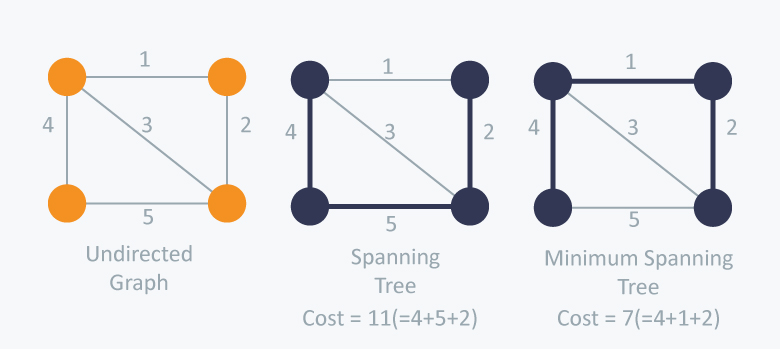
两种著名的查找最小生成树算法:克鲁斯卡尔算法和普里姆
Kruskal’s Algorithm
Kruskal采用了贪心算法。
- 将图的边按照权重排序。
- 从边的权重最小的开始添加,直到最大。
- 只添加连接未连通分量的边。
那么如果判断两个节点是否连接呢?
使用DFS的时间复杂度$ O(V+E) $,最好的算法是并查集,时间复杂度$ O(ElogV) $。(Disjoint Sets)
如:
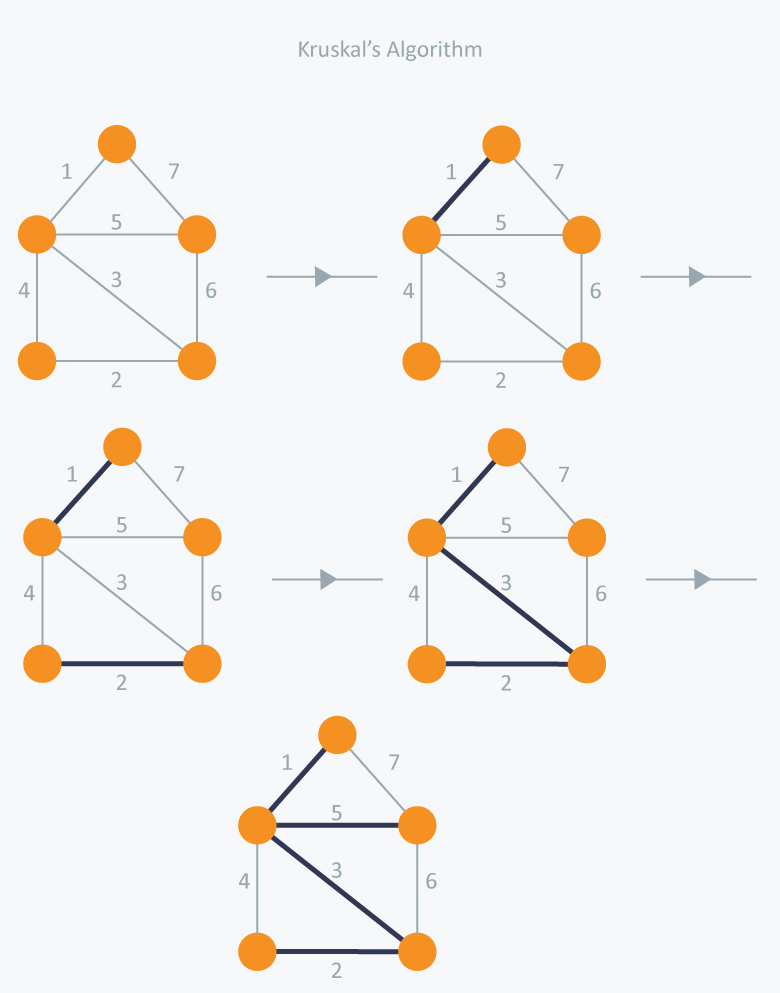
实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71
| #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <utility> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int MAX = 1e4 + 5; int id[MAX], nodes, edges; pair <long long, pair<int, int> > p[MAX]; void initialize() { for(int i = 0;i < MAX;++i) id[i] = i; } int root(int x) { while(id[x] != x) { id[x] = id[id[x]]; x = id[x]; } return x; } void union1(int x, int y) { int p = root(x); int q = root(y); id[p] = id[q]; } long long kruskal(pair<long long, pair<int, int> > p[]) { int x, y; long long cost, minimumCost = 0; for(int i = 0;i < edges;++i) { x = p[i].second.first; y = p[i].second.second; cost = p[i].first; if(root(x) != root(y)) { minimumCost += cost; union1(x, y); } } return minimumCost; } int main() { int x, y; long long weight, cost, minimumCost; initialize(); cin >> nodes >> edges; for(int i = 0;i < edges;++i) { cin >> x >> y >> weight; p[i] = make_pair(weight, make_pair(x, y)); } sort(p, p + edges); minimumCost = kruskal(p); cout << minimumCost << endl; return 0; } `
|
Prim’s Algorithm
Prim算法也使用贪心算法,不同的是Prim算法增加的是节点。时间复杂度$ O((V+E)logV) $
- 保持两个并查集,一个作为生成树。
- 选择连接当前生成树权重最小的节点,添加到生成树种。

1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56
| #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <functional> #include <utility> using namespace std; const int MAX = 1e4 + 5; typedef pair<long long, int> PII; bool marked[MAX]; vector <PII> adj[MAX]; long long prim(int x) { priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII> > Q; int y; long long minimumCost = 0; PII p; Q.push(make_pair(0, x)); while(!Q.empty()) { p = Q.top(); Q.pop(); x = p.second; if(marked[x] == true) continue; minimumCost += p.first; marked[x] = true; for(int i = 0;i < adj[x].size();++i) { y = adj[x][i].second; if(marked[y] == false) Q.push(adj[x][i]); } } return minimumCost; } int main() { int nodes, edges, x, y; long long weight, minimumCost; cin >> nodes >> edges; for(int i = 0;i < edges;++i) { cin >> x >> y >> weight; adj[x].push_back(make_pair(weight, y)); adj[y].push_back(make_pair(weight, x)); } minimumCost = prim(1); cout << minimumCost << endl; return 0; }
|
最短路径算法(Shortest Path Algorithms)
找到两个节点之间的最短路径,如果边的权重是1,可以使用BFS解决。
三种算法:贝尔曼算法、迪杰斯特拉算法和弗洛伊德算法
Bellman Ford’s Algorithm
最小的路径至少包含n-1条边,且不存在环。因为没必要经过一个节点2次。
时间复杂度:$ O(V*E) $
- 外层循环0~n-1
- 遍历所有的边,检查the next node distance > current node distance + edge weight。如果是, update the next node distance to “current node distance + edge weight”.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
| vector <int> v [2000 + 10]; int dis [1000 + 10]; for(int i = 0; i < m + 2; i++){ v[i].clear(); dis[i] = 2e9; } for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ scanf("%d%d%d", &from , next , &weight); v[i].push_back(from); v[i].push_back(next); v[i].push_back(weight); } dis[0] = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){ int j = 0; while(v[j].size() != 0){ if(dis[ v[j][0] ] + v[j][2] < dis[ v[j][1] ] ){ dis[ v[j][1] ] = dis[ v[j][0] ] + v[j][2]; } j++; } }
|
Dijkstra’s Algorithm
- 将所有的节点距离=无穷,除了开始节点distance=0
- 将source节点放在最小优先级队列中(distance,vertex)
- 最小优先级队列pop()一个节点,最开始时source节点
- 如果pop()的节点已经访问过,忽略
- 直到队列空
时间复杂度$ O(V+ElogV) $
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
| #definde SIZE 100000 + 1 vector < pair < int , int > > v [SIZE]; int dist [SIZE]; bool vis [SIZE]; void dijkstra(){ memset(vis, false , sizeof vis); dist[1] = 0; multiset < pair < int , int > > s; s.insert({0 , 1}); while(!s.empty()){ pair <int , int> p = *s.begin(); s.erase(s.begin()); int x = p.s; int wei = p.f; if( vis[x] ) continue; vis[x] = true; for(int i = 0; i < v[x].size(); i++){ int e = v[x][i].f; int w = v[x][i].s; if(dist[x] + w < dist[e] ){ dist[e] = dist[x] + w; s.insert({dist[e], e} ); } } } }
|
Floyd–Warshall’s Algorithm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++){ for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ dist[i][j] = min( dist[i][j], dist[i][k] + dist[k][j] ); } } }
|













