Recursion and Backtracking
方法自己调用自己的方法,叫做递归。就像电影 《盗梦空间》,梦中有梦。
1 2 3
| function dream() print "Dreaming" dream()
|
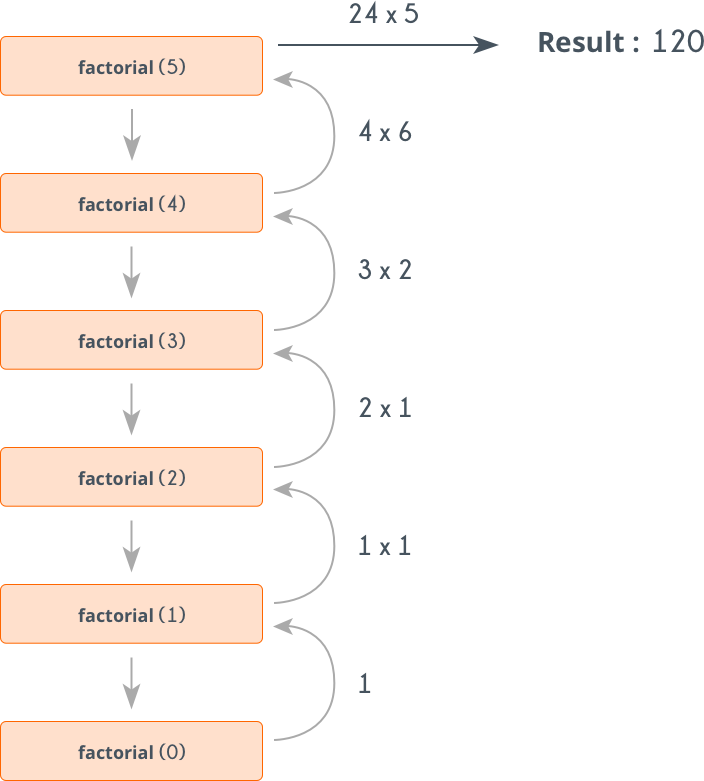
回溯法将问题分解成更小的通用的解法。每一个回溯方法必须有一个终止条件。终止条件是我们已经知道的结果。
1 2 3 4
| function factorial(x) if x is 0 return 1 return x*factorial(x-1)
|
使用回溯法的前提:
- 问题可以分成更小的通用的类型。
- 必须有终止条件。
- 在stackoverflow之前达到终止条件。
N-Queens Problem
给定一个N*N的棋盘,我们需要把N个皇后放在棋盘上,满足皇后不会被其他皇后攻击,水平,垂直,对角线会被攻击。
- 终止条件是N=0,返回成功解决问题。
- 当棋盘遍历结束但是N>0,需要回溯上一步。
伪代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
| is_attacked( x, y, board[][], N) if any cell in xth row is 1 return true if any cell in yth column is 1 return true if any cell (p, q) having p+q = x+y is 1 return true if any cell (p, q) having p-q = x-y is 1 return true return false N-Queens( board[][], N ) if N is 0 return true for i = 1 to N { for j = 1 to N { if is_attacked(i, j, board, N) is true skip it and move to next cell board[i][j] = 1 if N-Queens( board, N-1) is true return true board[i][j] = 0 were made i.e., remove current queen from (i,j)*/ } } return false
|
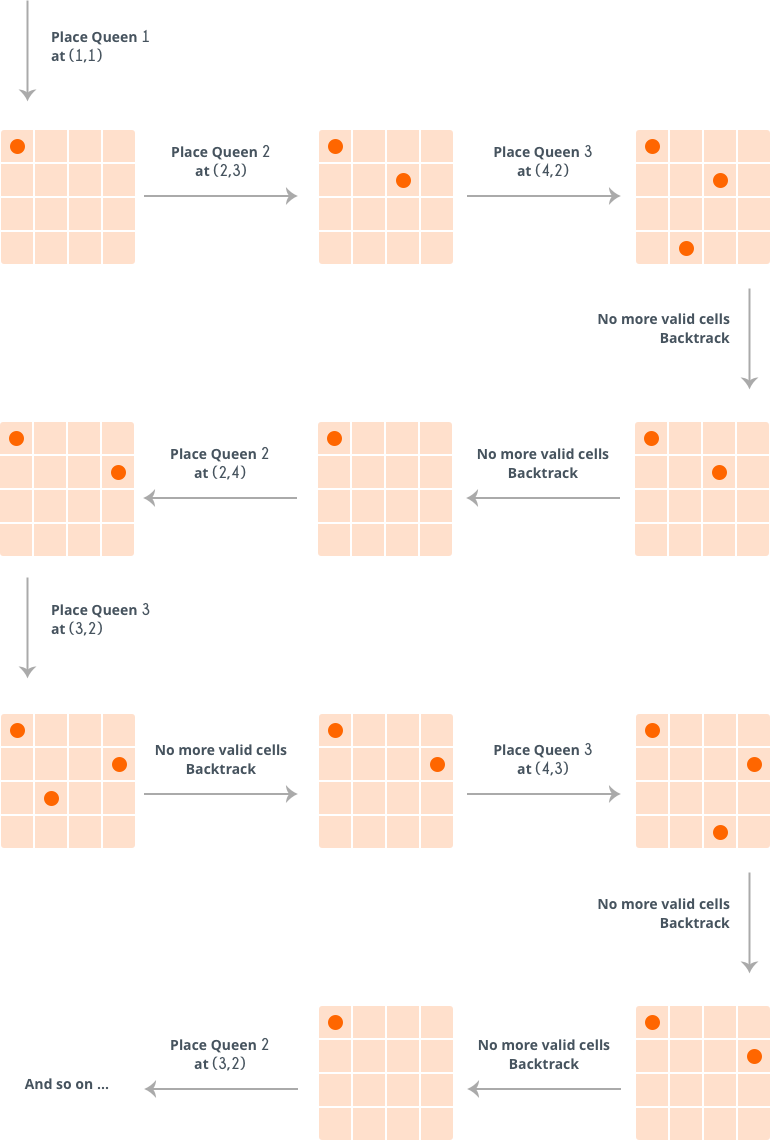
结果: