Linear Search
如果我们要查找数组中等于5的值,需要遍历数组。时间复杂度 $ O(N) $
Binary Serach
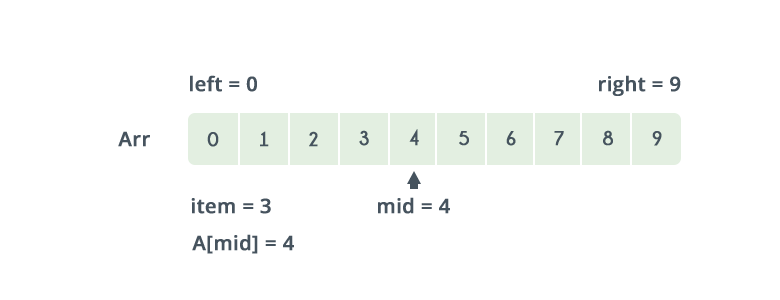
二分查找,前提是集合有序。
1 2 3
| Low = 0 High = n-1 Mid = (Low + High)/2
|
首先找到中间值比较,如果大于当前值,就往低处找,否则往高处找。直道当前值等于中间值。
时间复杂度:$ \log_2 N $
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
| int binarySearch(int low,int high,int key) { while(low<=high) { int mid=(low+high)/2; if(a[mid]<key) { low=mid+1; } else if(a[mid]>key) { high=mid-1; } else { return mid; } } return -1; }
|
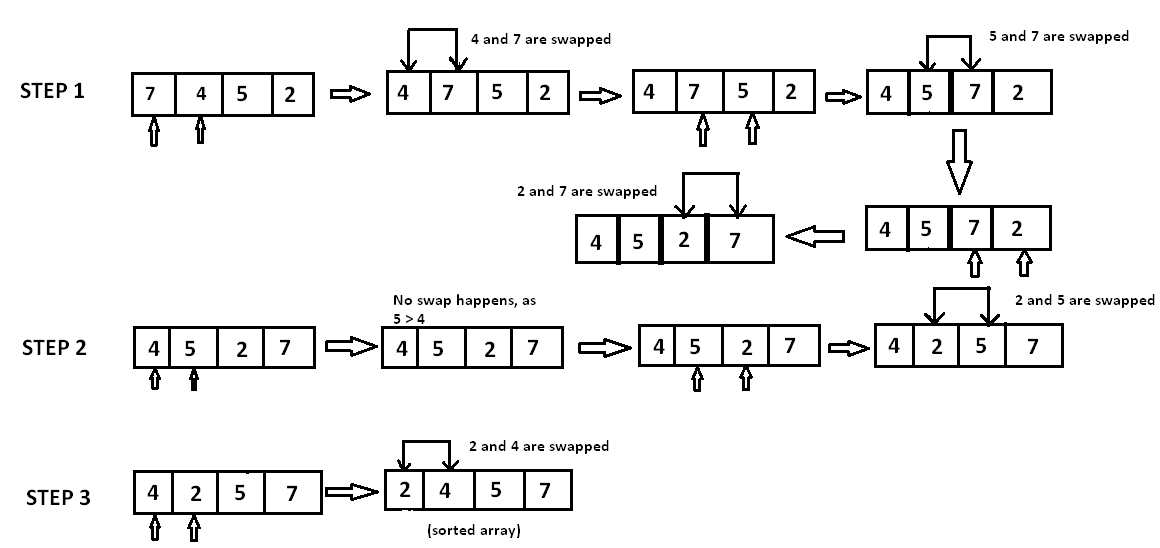
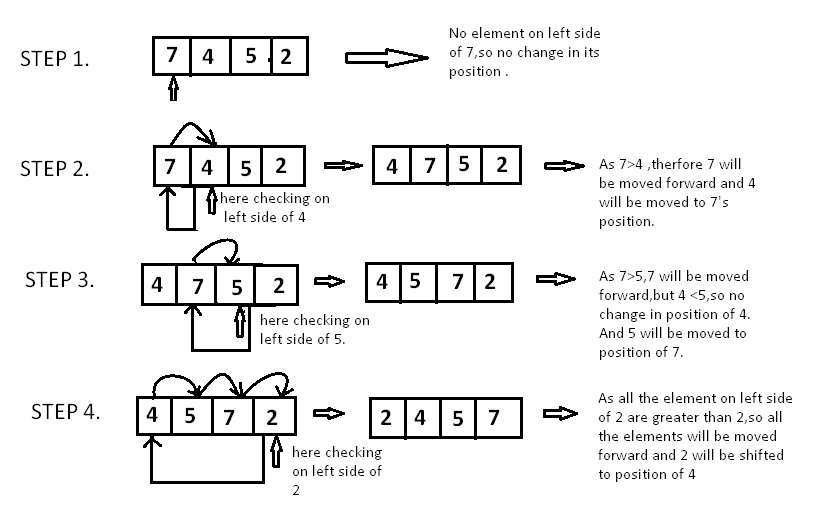
Bubble Sort
冒泡排序: 反复比较相邻的两个元素,如果顺序不对,就互相交换,直到集合有序。
每经过一趟排序,最大的值会冒到最后的位置。
时间复杂度:$ O(N^2) $
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
| void bubble_sort( int A[ ], int n ) { int temp; for(int k = 0; k< n-1; k++) { for(int i = 0; i < n-k-1; i++) { if(A[ i ] > A[ i+1] ) { temp = A[ i ]; A[ i ] = A[ i+1 ]; A[ i + 1] = temp; } } } }
|
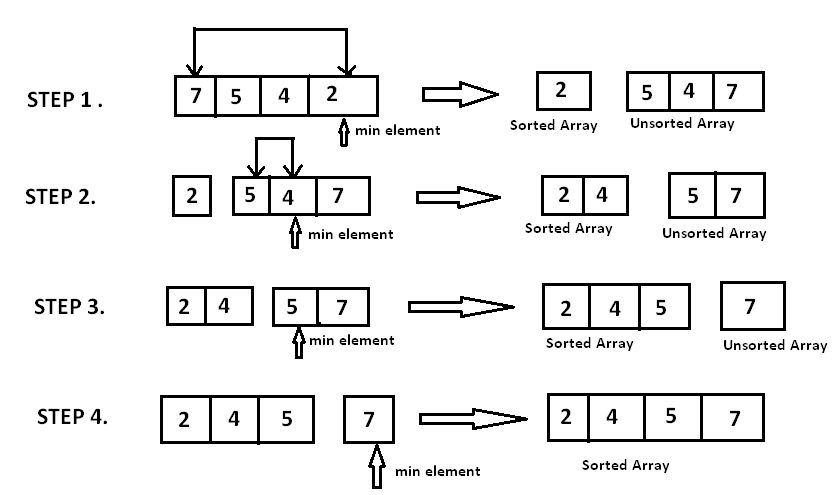
Selection Sort
选择排序:找到当前最大的元素,放到正确的位置上,使集合有序。
时间复杂度:$ O(N^2) $
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
| void selection_sort (int A[ ], int n) { // temporary variable to store the position of minimum element int minimum; // reduces the effective size of the array by one in each iteration. for(int i = 0; i < n-1 ; i++) { // assuming the first element to be the minimum of the unsorted array . minimum = i ; // gives the effective size of the unsorted array . for(int j = i+1; j < n ; j++ ) { if(A[ j ] < A[ minimum ]) { //finds the minimum element minimum = j ; } } // putting minimum element on its proper position. swap ( A[ minimum ], A[ i ]) ; } }
|
Insertion Sort
插入排序:假设开始只有一个元素,集合是有序的,取之后的元素,遍历已经有序集合,找到当前元素的正确位置,并插入。
时间按复杂度:$ O(N^2) $
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
| void insertion_sort ( int A[ ] , int n) { for( int i = 0 ;i < n ; i++ ) { correct position .*/ int temp = A[ i ]; int j = i; less than the current element. */ while( j > 0 && temp < A[ j -1]) { A[ j ] = A[ j-1]; j= j - 1; } A[ j ] = temp; } }
|
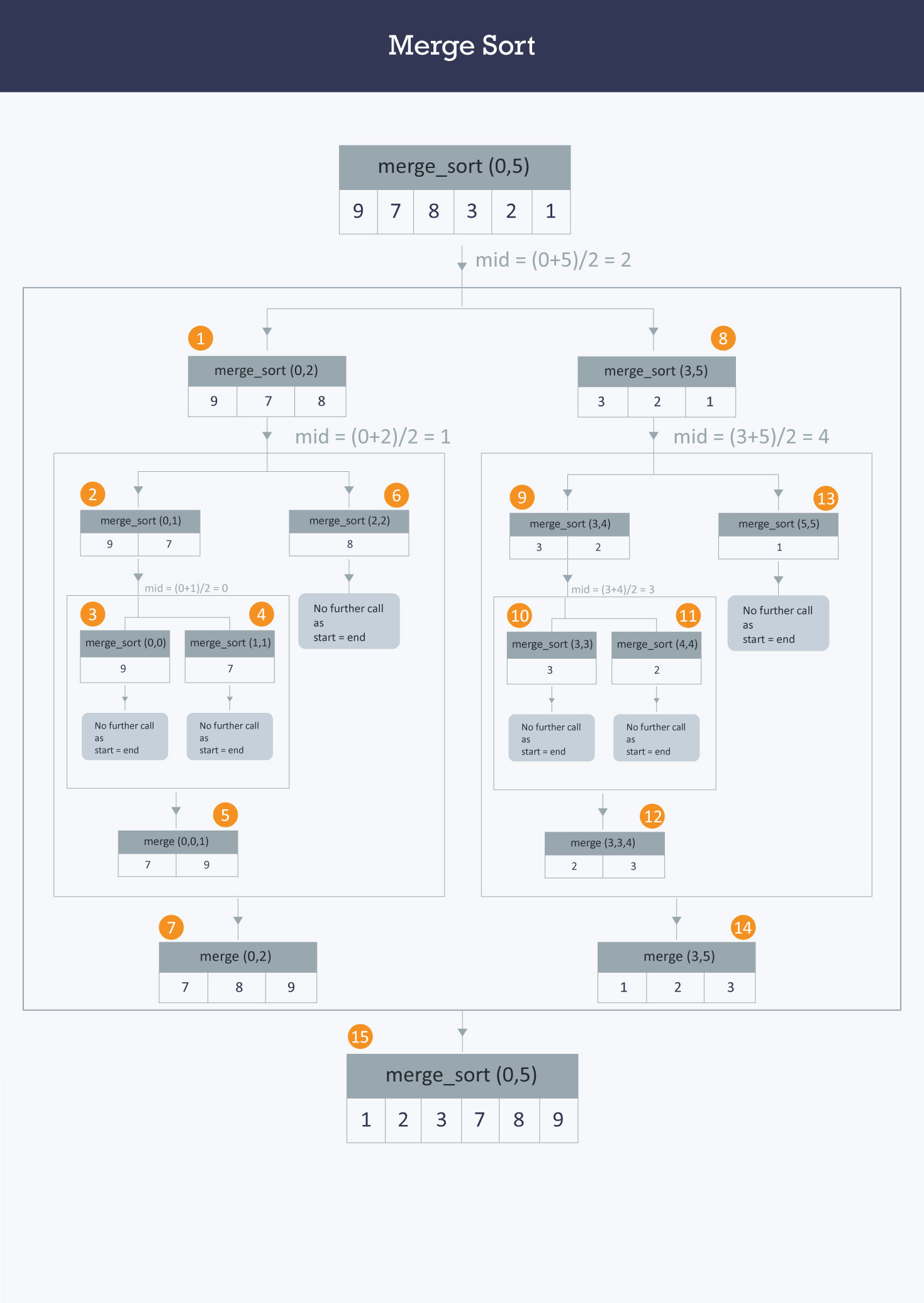
Merge Sort
归并排序 :是基于分治算法的,将当前集合分成几个更小的子集,直到子集只包含一个元素,那么自己是有序的,然后合并自己,直到整个集合有序。
时间复杂度:$ O(NlogN) $
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
| void merge(int A[ ] , int start, int mid, int end) { int p = start ,q = mid+1; int Arr[end-start+1] , k=0; for(int i = start ;i <= end ;i++) { if(p > mid) Arr[ k++ ] = A[ q++] ; else if ( q > end) Arr[ k++ ] = A[ p++ ]; else if( A[ p ] < A[ q ]) Arr[ k++ ] = A[ p++ ]; else Arr[ k++ ] = A[ q++]; } for (int p=0 ; p< k ;p ++) { parts.*/ A[ start++ ] = Arr[ p ] ; } }
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| void merge_sort (int A[ ] , int start , int end ) { if( start < end ) { int mid = (start + end ) / 2 ; merge_sort (A, start , mid ) ; merge_sort (A,mid+1 , end ) ; merge(A,start , mid , end ); } }
|
Quick Sort
快排:基于分治算法。随机选择一个元素,将大于这个元素和小于这个元素分成两个集合,直到集合只有一个元素
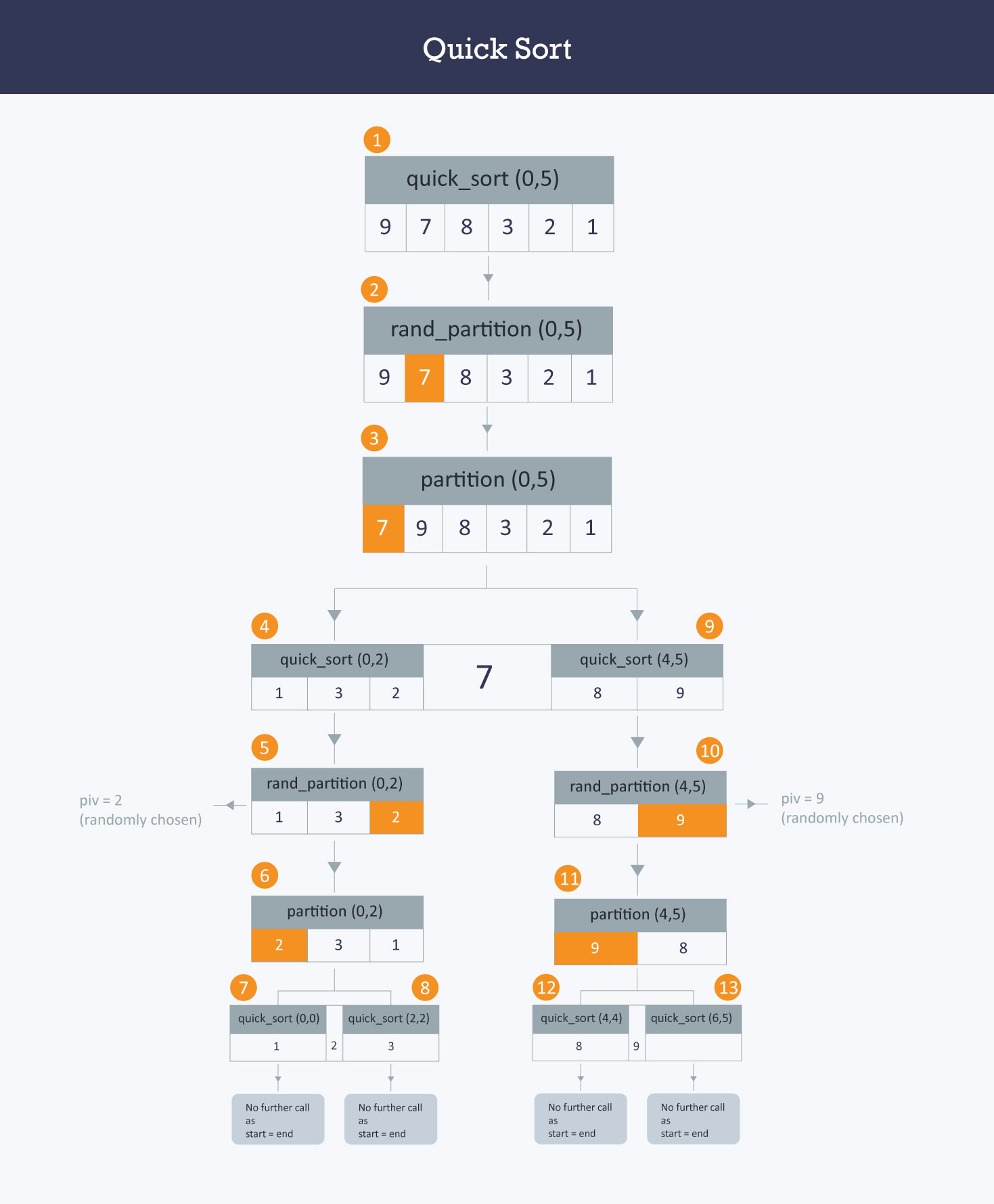
随机选择一个元素7,与第一个元素交换
将7作为基准
1<7 9="" 1,9,8,3,2,7="">7 1,7,8,3,2,9
2<7 8="" 1,2,8,3,7,9="">7 1,2,7,3,8,9
3<7 1,2,3,7,8,9
这时[1,2,3] 7 [8,9]
随机选择2作为基点,与第一个交换2,1,3
3>1
1<2 1,2,3
这时1[2]3 有序
随机选择9作为基点,与第一个交换9,8
8<9 8,9
这时有序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| int rand_partition ( int A[ ] , int start , int end ) { int random = start + rand( )%(end-start +1 ) ; swap ( A[random] , A[start]) ; return partition(A,start ,end) ; }
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
| int partition ( int A[],int start ,int end) { int i = start + 1; int piv = A[start] ; for(int j =start + 1; j <= end ; j++ ) { on one side and which are greater that on other. */ if ( A[ j ] < piv) { swap (A[ i ],A [ j ]); i += 1; } } swap ( A[ start ] ,A[ i-1 ] ) ; return i-1; }
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
| void quick_sort ( int A[ ] ,int start , int end ) { if( start < end ) { int piv_pos = partition (A,start , end ) ; quick_sort (A,start , piv_pos -1); quick_sort ( A,piv_pos +1 , end) ; } }
|
Greedy Algorithms
面对不同的问题,需要不同的算法。
常用的算法:
- 分治算法
- 随机算法
- 贪心算法(确切地说应该是一种技术)
- 动态规划
贪婪算法 : 总是选择当前最优解。不会反悔已经做得决定。
优点:容易找到解决问题的方法,容易计算时间复杂度。
缺点:很难证明结果的正确性。
如:
有一个数组A,A中每一个数字代表任务花费的时间,计算T时间内最多能做几件事。
- 将数组A按升序排序。
- 遍历数组,累加每一个任务花费的时间,直到大于T。







